基于 Redis 实现 Laravel 消息队列系统及底层源码探究
消息队列简介
一个完整的队列系统由以下三个组件组成:
- 队列(Queue)
- 消息(Message)
- 处理进程(Worker)
对应的基本工作流程是生产者(业务代码)先将消息数据推送到队列,然后再通过其他的处理进程来消费队列中的消息数据,从而实现生产者和消费者之间的解耦。因此,消息队列非常适用于一些需要异步执行的耗时操作(比如邮件发送、文件上传),或者业务临时的高并发操作(比如秒杀、消息推送),对于提升系统性能和负载非常有效,尤其是 PHP 这种本身不支持并发编程的语言,是实现异步编程的不二之选。
在演示如何实现消息队列之前,我们先来简单介绍下上面的三个组件。
队列
队列其实是一种线性的数据结构,这一点学院君在数据结构篇中已经详细介绍过,这种数据结构有先入先出(FIFO)的特点,因此很适合做生产者和消费者之间的解耦,同时不影响业务逻辑的执行顺序。
在 PHP 中,可以使用原生的数组函数或者 SplQueue 类很轻松地实现队列这种数据结构,不过这里我们介绍的是 Redis,所以还可以借助 Redis 自带的列表类型来实现。
我们可以将上篇教程中的文章浏览数更新操作通过队列异步实现来提升系统性能。为了简化流程,我们通过 post-views-increment 来标识队列名称,推送到队列的消息数据通过文章 ID 进行标识:
// 文章浏览数 +1
public function addViews(Post $post)
{
// 推送消息数据到队列,通过异步进程处理数据库更新
Redis::rpush('post-views-increment', $post->id);
return ++$post->views;
}
消息
所谓消息,即推送到队列中的数据,通常是一个字符串,如果是非字符串类型,可以通过序列化操作将其转化为字符串,消费端的处理进程从队列中取出消息数据后,可以对其进行解析处理,完成业务逻辑的闭环。
生产者或者消息本身不必关心消费端处理进程如何处理消息数据,消费端的处理进程也不必关心是谁发送的消息,三者是完全解耦的,但是又通过消息数据架起了生产者和消费者之间的桥梁。
消息数据可以在应用内部传递,也可以跨应用传递,跨应用传递通常需要借助第三方的消息队列中间件,比如基于 Redis 实现的队列系统、RabbitMQ、Kafka、RocketMQ 等。
在上面的示例代码中,我们将文章 ID 作为消息数据进行传递。
处理进程
消费端的处理进程通常是一个或者多个常驻内存的进程,它们或订阅或轮询消息队列,如果消息队列不为空,则取出其中的消息数据进行处理。
这里为了简化流程,我们创建一个 Artisan 命令来模拟一个常驻内存的轮询进程作为消息处理器:
php artisan make:command MockQueueWorker
并编写其实现代码如下:
<?php
namespace App\Console\Commands;
use App\Models\Post;
use Illuminate\Console\Command;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Redis;
class MockQueueWorker extends Command
{
/**
* The name and signature of the console command.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $signature = 'mock:queue-worker';
/**
* The console command description.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $description = 'Mock Queue Worker';
/**
* Create a new command instance.
*
* @return void
*/
public function __construct()
{
parent::__construct();
}
/**
* Execute the console command.
*
* @return int
*/
public function handle()
{
$this->info('监听消息队列 post-views-increment...');
while (true) {
// 从队列中取出消息数据
$postId = Redis::lpop('post-views-increment');
// 将当前文章浏览数 +1,并存储到对应 Sorted Set 的 score 字段
if ($postId && Post::newQuery()->where('id', $postId)->increment('views')) {
Redis::zincrby('popular_posts', 1, $postId);
$this->info("更新文章 #{$postId} 的浏览数");
}
}
}
}
重点关注 handle 方法,我们通过 while (true) 模拟常驻内存,然后不断轮询 post-views-increment 队列,如果其中有文章 ID 数据,则取出并更新文章浏览数。
这样一来,我们就实现了一个简单的消息队列,启动这个消息处理器:

然后访问任意一篇文章 http://redis.test/posts/1,就可以在队列处理器窗口看到队列的任务处理记录:

同时在数据库中看到更新后的浏览数,证明队列消息处理成功。
以上流程也是 Laravel 队列系统底层实现的基本原理,有了这个知识储备,接下来看 Laravel 消息队列底层实现会轻松很多。
Laravel 队列系统实现和使用
基本配置
不过,Laravel 提供了更优雅的队列系统实现,不需要我们手动去编写队列、消息和处理进程的实现代码,并且支持不同的队列系统驱动,包括数据库、Beanstalkd、Amazon SQS、Redis 等,这里我们当然以 Redis 为例进行演示。
要在 Laravel 项目中使用 Redis 实现队列系统,只需在配置好 Redis 连接信息后将环境配置文件 .env 中的 QUEUE_CONNECTION 配置值调整为 redis 即可:
QUEUE_CONNECTION=redis
这样一来,Laravel 就可以基于 config/queue.php 中的 redis 配置初始化队列系统了:
'redis' => [
'driver' => 'redis',
'connection' => 'default',
'queue' => env('REDIS_QUEUE', 'default'),
'retry_after' => 90,
'block_for' => null,
],
队列系统服务提供者
在 Laravel 应用启动时,会通过 QueueServiceProvider 来注册队列系统相关服务到服务容器:
public function register()
{
$this->registerManager();
$this->registerConnection();
$this->registerWorker();
$this->registerListener();
$this->registerFailedJobServices();
}
...
// 队列管理器
protected function registerManager()
{
$this->app->singleton('queue', function ($app) {
return tap(new QueueManager($app), function ($manager) {
$this->registerConnectors($manager);
});
});
}
// 默认队列连接,这里根据配置值会初始化为 redis 连接
protected function registerConnection()
{
$this->app->singleton('queue.connection', function ($app) {
return $app['queue']->connection();
});
}
// 队列处理器
protected function registerWorker()
{
$this->app->singleton('queue.worker', function ($app) {
$isDownForMaintenance = function () {
return $this->app->isDownForMaintenance();
};
return new Worker(
$app['queue'],
$app['events'],
$app[ExceptionHandler::class],
$isDownForMaintenance
);
});
}
// 队列监听器,监听队列事件
protected function registerListener()
{
$this->app->singleton('queue.listener', function ($app) {
return new Listener($app->basePath());
});
}
// 失败任务处理(默认基于数据库)
protected function registerFailedJobServices()
{
$this->app->singleton('queue.failer', function ($app) {
$config = $app['config']['queue.failed'];
if (isset($config['driver']) && $config['driver'] === 'dynamodb') {
return $this->dynamoFailedJobProvider($config);
} elseif (isset($config['driver']) && $config['driver'] === 'database-uuids') {
return $this->databaseUuidFailedJobProvider($config);
} elseif (isset($config['table'])) {
return $this->databaseFailedJobProvider($config);
} else {
return new NullFailedJobProvider;
}
});
}
RedisQueue 队列实现
底层代码设计和缓存类似 —— 基于 QueueManager 管理不同驱动的队列系统连接,最终的消息推送和接收则根据当前使用的队列驱动分发到对应的队列系统去处理,这里配置使用 Redis 作为消息系统驱动,所以最终会通过 RedisConnector 连接到 RedisQueue 去处理:
/**
* 建立队列连接
*
* @param array $config
* @return \Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\Queue
*/
public function connect(array $config)
{
return new RedisQueue(
$this->redis, $config['queue'],
$config['connection'] ?? $this->connection,
$config['retry_after'] ?? 60,
$config['block_for'] ?? null
);
}
你可以在 RedisQueue 中看到推送消息数据到队列的实现方法 push:
public function push($job, $data = '', $queue = null)
{
return $this->enqueueUsing(
$job,
$this->createPayload($job, $this->getQueue($queue), $data),
$queue,
null,
function ($payload, $queue) {
return $this->pushRaw($payload, $queue);
}
);
}
public function pushRaw($payload, $queue = null, array $options = [])
{
$this->getConnection()->eval(
LuaScripts::push(), 2, $this->getQueue($queue),
$this->getQueue($queue).':notify', $payload
);
return json_decode($payload, true)['id'] ?? null;
}
Laravel 使用任务类作为消息数据的默认格式,由于是对象类型,所以会做序列化处理,最终的推送操作使用了 Lua 脚本通过 Reis RPUSH 指令完成:
public static function push()
{
return <<<'LUA'
-- Push the job onto the queue...
redis.call('rpush', KEYS[1], ARGV[1])
-- Push a notification onto the "notify" queue...
redis.call('rpush', KEYS[2], 1)
LUA;
}
这里的队列连接是 Redis,其默认的队列是 default。从消息队列中读取数据使用了 pop 方法实现:
public function pop($queue = null)
{
$this->migrate($prefixed = $this->getQueue($queue));
if (empty($nextJob = $this->retrieveNextJob($prefixed))) {
return;
}
[$job, $reserved] = $nextJob;
if ($reserved) {
return new RedisJob(
$this->container, $this, $job,
$reserved, $this->connectionName, $queue ?: $this->default
);
}
}
...
protected function retrieveNextJob($queue, $block = true)
{
$nextJob = $this->getConnection()->eval(
LuaScripts::pop(), 3, $queue, $queue.':reserved', $queue.':notify',
$this->availableAt($this->retryAfter)
);
if (empty($nextJob)) {
return [null, null];
}
[$job, $reserved] = $nextJob;
if (! $job && ! is_null($this->blockFor) && $block &&
$this->getConnection()->blpop([$queue.':notify'], $this->blockFor)) {
return $this->retrieveNextJob($queue, false);
}
return [$job, $reserved];
}
在获取数据的 Lua 脚本中使用了 Redis LPOP 指令,具体代码就不贴出来了,队列连接是 Redis,默认队列是 default。
虽然看起来这个底层实现很复杂,但是基本原理和我们上面通过 Redis 原生代码实现是一致的。当然了,Laravel 还支持一些更复杂的操作,比如延迟推送、批处理等,你可以自行研究 RedisQueue 中对应的实现源码了解底层细节。
消息数据
Laravel 队列系统中的消息数据会以任务类形式提供,并且针对不同的驱动再做一层封装,从而方便底层进行统一处理,对于 Redis 驱动的队列系统,最终获取到的数据会通过 RedisJob 封装后返回,RedisJob 的构造函数如下所示:
public function __construct(Container $container, RedisQueue $redis, $job, $reserved, $connectionName, $queue)
{
$this->job = $job;
$this->redis = $redis;
$this->queue = $queue;
$this->reserved = $reserved;
$this->container = $container;
$this->connectionName = $connectionName;
$this->decoded = $this->payload();
}
其中 $job 对应的是业务代码推送到队列的任务类实例,$this->payload() 中返回的是反序列化后的任务类负荷数据,其余字段则是底层根据消息队列配置自动获取的。
异步处理进程
Laravel 提供了多个 Artisan 命令来处理消息队列,这些 Artisan 命令的源码位于 vendor/laravel/framework/src/Illuminate/Queue/Console 目录下:
你可以通过 queue:work 或者 queue:listen 命令来监听并处理消息队列中的数据,以 queue:work 为例,对应的源码位于 WorkCommand 中,我们重点关注 handle 方法的实现:
public function handle()
{
if ($this->downForMaintenance() && $this->option('once')) {
return $this->worker->sleep($this->option('sleep'));
}
$this->listenForEvents();
$connection = $this->argument('connection')
?: $this->laravel['config']['queue.default'];
$queue = $this->getQueue($connection);
return $this->runWorker(
$connection, $queue
);
}
如果系统处于维护模式,则不消费任何队列,否则的话调用 listenForEvents 方法监听队列事件并输出日志到命令行:
protected function listenForEvents()
{
$this->laravel['events']->listen(JobProcessing::class, function ($event) {
$this->writeOutput($event->job, 'starting');
});
$this->laravel['events']->listen(JobProcessed::class, function ($event) {
$this->writeOutput($event->job, 'success');
});
$this->laravel['events']->listen(JobFailed::class, function ($event) {
$this->writeOutput($event->job, 'failed');
$this->logFailedJob($event);
});
}
然后从队列配置中获取到当前队列连接和默认队列,这里配置的是 Redis 队列连接,其默认的队列是 default,获取到队列系统信息后,就可以调用 runWorker 方法运行消费端处理进程了:
protected function runWorker($connection, $queue)
{
return $this->worker->setName($this->option('name'))
->setCache($this->cache)
->{$this->option('once') ? 'runNextJob' : 'daemon'}(
$connection, $queue, $this->gatherWorkerOptions()
);
}
这里的 $this->worker 对应的是 Laravel 在 QueueServiceProvider 中注册的 queue.worker,即 Worker 类实例,如果是一次性执行的话(通过 --once 选项指定),则调用 Worker 类的 runNextJob 方法:
public function runNextJob($connectionName, $queue, WorkerOptions $options)
{
$job = $this->getNextJob(
$this->manager->connection($connectionName), $queue
);
if ($job) {
return $this->runJob($job, $connectionName, $options);
}
$this->sleep($options->sleep);
}
这里获取消息队列中任务数据的 getNextJob 方法正是调用了前面 RedisQueue(这里配置的是 Redis 队列,其他驱动以此类推)的 pop 方法返回的通过 RedisJob 封装后的消息数据,然后调用 runJob 方法对这个表征消息数据的任务类进行处理:
protected function runJob($job, $connectionName, WorkerOptions $options)
{
try {
return $this->process($connectionName, $job, $options);
} catch (Throwable $e) {
$this->exceptions->report($e);
$this->stopWorkerIfLostConnection($e);
}
}
这里的 process 方法会调用 RedisJob 上定义的 fire 方法执行对应的任务逻辑(更底层调用的是 Redis 封装任务类上的处理方法):
public function process($connectionName, $job, WorkerOptions $options)
{
try {
$this->raiseBeforeJobEvent($connectionName, $job);
$this->markJobAsFailedIfAlreadyExceedsMaxAttempts(
$connectionName, $job, (int) $options->maxTries
);
if ($job->isDeleted()) {
return $this->raiseAfterJobEvent($connectionName, $job);
}
$job->fire();
$this->raiseAfterJobEvent($connectionName, $job);
} catch (Throwable $e) {
$this->handleJobException($connectionName, $job, $options, $e);
}
}
如果不是一次性执行的话,则调用的是 Worker 类的 daemon 方法:
public function daemon($connectionName, $queue, WorkerOptions $options)
{
if ($this->supportsAsyncSignals()) {
$this->listenForSignals();
}
$lastRestart = $this->getTimestampOfLastQueueRestart();
[$startTime, $jobsProcessed] = [hrtime(true) / 1e9, 0];
while (true) {
if (! $this->daemonShouldRun($options, $connectionName, $queue)) {
$status = $this->pauseWorker($options, $lastRestart);
if (! is_null($status)) {
return $this->stop($status);
}
continue;
}
$job = $this->getNextJob(
$this->manager->connection($connectionName), $queue
);
if ($this->supportsAsyncSignals()) {
$this->registerTimeoutHandler($job, $options);
}
if ($job) {
$jobsProcessed++;
$this->runJob($job, $connectionName, $options);
} else {
$this->sleep($options->sleep);
}
if ($this->supportsAsyncSignals()) {
$this->resetTimeoutHandler();
}
$status = $this->stopIfNecessary(
$options, $lastRestart, $startTime, $jobsProcessed, $job
);
if (! is_null($status)) {
return $this->stop($status);
}
}
}
和 runNextJob 类似,只是在外层包裹了 while(true) 实现常驻进程,以及其它的保障程序稳健性的代码。
任务类推送和处理的完整链路
了解了 Laravel 队列系统底层实现原理后,我们再来看如何在业务代码中使用它。还是以文章浏览数更新为例,按照队列->消息->处理进程三个组件循序实现,方便对比理解。
对于队列系统,通过 QUEUE_CONNECTION 配置你想要使用的队列驱动即可,这里已经配置成了 redis,Laravel 底层会使用 RedisQueue 这个队列实现,不需要编写任务额外的代码。
当然了,除了 Laravel 自带的队列驱动之外,你还可以参照这些内置实现自定义队列系统驱动。
然后定义一个任务类作为推送到队列系统的消息数据,Laravel 提供了 make:job Artisan 命令来快速生成任务类:
php artisan make:job PostViewsIncrement
其实你也可以通过
Queue::pushRaw(string)推送原生字符串格式消息数据到 Redis 队列,但是 Laravel 提供的处理进程不知道该怎么处理这个消息,所以一般不这么做,如果你定义了对字符串格式消息的处理逻辑,则未尝不可。
编写该任务类的实现代码如下,将文章浏览数更新业务代码迁移到 handle 方法中实现即可:
<?php
namespace App\Jobs;
use App\Models\Post;
use Illuminate\Bus\Queueable;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\ShouldQueue;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Bus\Dispatchable;
use Illuminate\Queue\InteractsWithQueue;
use Illuminate\Queue\SerializesModels;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Redis;
class PostViewsIncrement implements ShouldQueue
{
use Dispatchable, InteractsWithQueue, Queueable, SerializesModels;
public Post $post;
/**
* Create a new job instance.
*
* @param Post $post
*/
public function __construct(Post $post)
{
$this->post = $post;
}
/**
* Execute the job.
*
* @return void
*/
public function handle()
{
if ($this->post->increment('views')) {
Redis::zincrby('popular_posts', 1, $this->post->id);
}
}
}
定义好任务类后,可以在控制器中通过 dispatch 辅助函数分发这个任务类将其推送到队列系统:
// 浏览文章
public function show($id)
{
$post = $this->postRepo->getById($id);
// 分发队列任务
$this->dispatch(new PostViewsIncrement($post));
return "Show Post #{$post->id}, Views: {$post->views}";
}
该函数最终会通过 Illuminate\Bus\Dispatcher 的 dispatch 方法分发任务类:
public function dispatch($command)
{
return $this->queueResolver && $this->commandShouldBeQueued($command)
? $this->dispatchToQueue($command)
: $this->dispatchNow($command);
}
如果传入的 $command 参数是一个实现了 ShouldQueue 接口的实例,则调用 dispatchToQueue 方法将其推送到指定队列:
public function dispatchToQueue($command)
{
$connection = $command->connection ?? null;
$queue = call_user_func($this->queueResolver, $connection);
if (! $queue instanceof Queue) {
throw new RuntimeException('Queue resolver did not return a Queue implementation.');
}
if (method_exists($command, 'queue')) {
return $command->queue($queue, $command);
}
return $this->pushCommandToQueue($queue, $command);
}
这里解析到的 queue 变量是 RedisQueue 实例,如果任务类定义了 queue 方法,则使用该方法定义的代码推送任务类队列,否则调用 pushCommandToQueue 方法推送:
protected function pushCommandToQueue($queue, $command)
{
if (isset($command->queue, $command->delay)) {
return $queue->laterOn($command->queue, $command->delay, $command);
}
if (isset($command->queue)) {
return $queue->pushOn($command->queue, $command);
}
if (isset($command->delay)) {
return $queue->later($command->delay, $command);
}
return $queue->push($command);
}
如果没有延迟推送的设置,任务类也没有设置 queue 属性,则调用 $queue->push($command) 方法推送任务类到队列,也就是我们上面介绍的 RedisQueue 上的 push 方法。
实际上,直接通过
Queue::push(new PostViewsIncrement($post))也可以推送任务类到 Redis 队列,不过使用dispatch方式更加优雅、稳健,不需要我们额外去处理任务类校验、延迟推送如何处理、如何推送到自定义队列、应用队列消息处理中间件等,所以我们在日常开发中使用dispatch方法推送即可。
任务类(消息数据)推送成功后,就可以通过 Laravel 提供的 Artisan 命令 queue:work 作为处理进程来监听并消费队列中的任务类了:
php artisan queue:work
在浏览器中访问文章,就可以在终端窗口看到对应消息队列处理结果。

如果你在队列消息被处理之前去查看其数据结构(默认位于 laravel_database_queues:default 中):
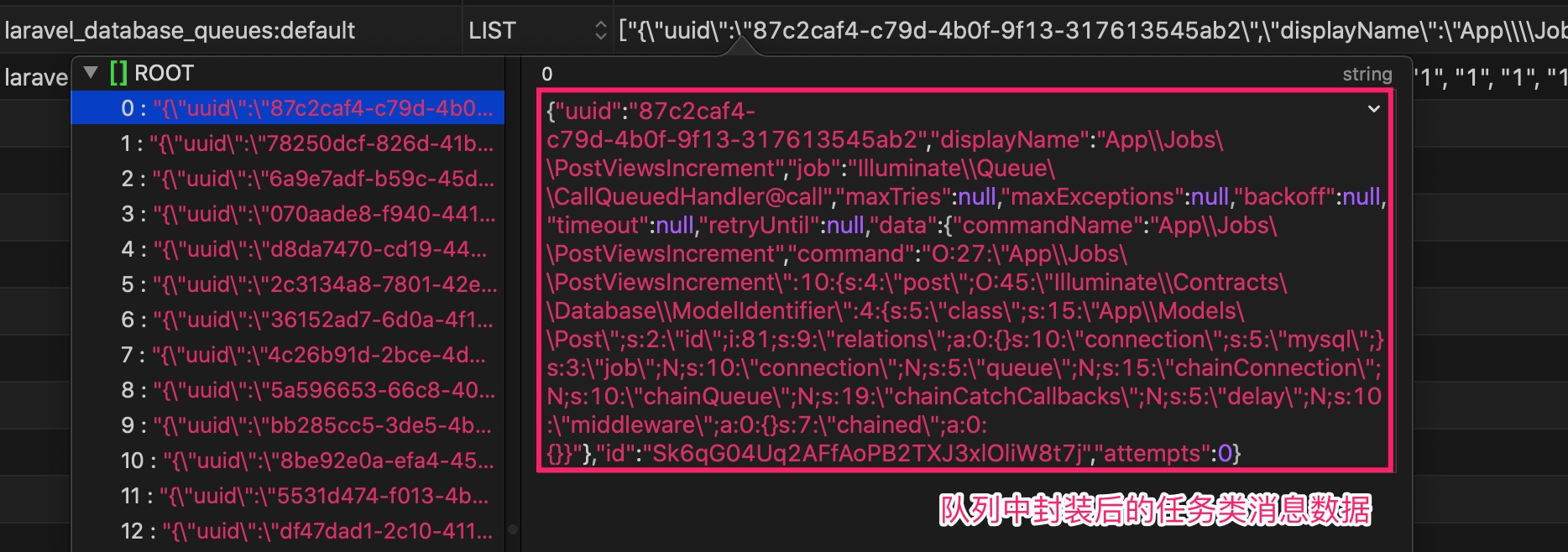
可以看到这个是一个经过 JSON 序列化后的消息数据:

job 对应的是如何处理这个消息数据,最终执行的则是 data.command 中 unserialize 出来的 PostViewsIncrement 对象上的 handle 方法。
回顾下上面异步处理进程中最终执行的是任务类 RedisJob 实例上的 fire 方法,其源码如下所示:
public function fire()
{
$payload = $this->payload();
[$class, $method] = JobName::parse($payload['job']);
($this->instance = $this->resolve($class))->{$method}($this, $payload['data']);
}
这里的 payload 就是 Redis 队列中的 JSON 格式消息数据了,我们通过 job 字段值解析出消息数据处理器,然后将 data 字段值(即包含 PostViewsIncrement 任务类实例的数据)作为参数传递进去,CallQueuedHandler 的 call 最终也会基于 Dispatcher 分发任务类执行,在此之前还会执行任务类中定义的中间件:
public function call(Job $job, array $data)
{
try {
$command = $this->setJobInstanceIfNecessary(
$job, unserialize($data['command'])
);
} catch (ModelNotFoundException $e) {
return $this->handleModelNotFound($job, $e);
}
...
$this->dispatchThroughMiddleware($job, $command);
...
}
protected function dispatchThroughMiddleware(Job $job, $command)
{
return (new Pipeline($this->container))->send($command)
->through(array_merge(method_exists($command, 'middleware') ? $command->middleware() : [], $command->middleware ?? []))
->then(function ($command) use ($job) {
return $this->dispatcher->dispatchNow(
$command, $this->resolveHandler($job, $command)
);
});
}
如果这个任务类有对应的处理器类,则通过处理器类运行,否则调用这个任务类本身提供的 handle 或者 __invoke 方法执行,这里也就是我们在 PostViewsIncrement 上定义的 handle 方法:
public function dispatchNow($command, $handler = null)
{
$uses = class_uses_recursive($command);
if (in_array(InteractsWithQueue::class, $uses) &&
in_array(Queueable::class, $uses) &&
! $command->job) {
$command->setJob(new SyncJob($this->container, json_encode([]), 'sync', 'sync'));
}
if ($handler || $handler = $this->getCommandHandler($command)) {
$callback = function ($command) use ($handler) {
$method = method_exists($handler, 'handle') ? 'handle' : '__invoke';
return $handler->{$method}($command);
};
} else {
$callback = function ($command) {
$method = method_exists($command, 'handle') ? 'handle' : '__invoke';
return $this->container->call([$command, $method]);
};
}
return $this->pipeline->send($command)->through($this->pipes)->then($callback);
}
到这里,我们就把 Laravel 基于 Redis 的队列系统实现中,代表消息数据的任务类从定义,到分发,到被推送到队列,最后再通过 Artisan 命令异步消费处理的完整链路给大家展示了一遍,相信你应该对队列系统的底层实现以及上层使用了然于胸了:队列系统和异步处理 Laravel 框架都已经提供了,在日常开发时,我们只需要按照消息任务类的结构编写 handle 处理方法,然后在适当的地方通过 dispatch 方法进行分发即可,剩下的交给 Laravel 去处理就好了,就是这么简单。
你可以参考 Laravel 队列文档了解更多 Laravel 队列使用细节,除此之外,Laravel 还提供了一个适用于 Redis 队列系统的一体化解决方案 —— Horizon,推荐在生产环境使用它作为 Redis 消息队列系统解决方案,学院君后面会单独开一个消息队列的专题系统介绍所有这些功能特性的使用以及部署。
使用队列系统的好处
在这篇教程的开头,学院君已经给大家介绍了使用消息队列的优势,我们在其基础上做一个总结:
- 将生产者和消费者分离,实现代码解耦,提高系统容错率(消费端处理失败后,可以重复多次处理消息数据,直到执行成功);
- 消费端处理进程可以异步处理消息数据,从而有效提升系统响应速度,增强用户体验,这对一些耗时任务优化效果很显著(比如邮件发送、数据库操作、文件存储、爬虫之类的 IO 密集型操作);
- 除了 IO 密集型操作,还可以对 CPU 密集型操作进行优化,比如启动多个处理进程将一个大的耗时任务拆分成多个子任务执行,消息队列可以看做是 PHP 异步和并发编程的一种补充实现;
- 由于队列先入先出的特点,因此可以确保同一个队列中的任务可以按照指定序列执行,而不像一般并发编程那样不能确保子任务的执行顺序;
- 由于消息队列中间件(这里是 Redis)可以独立于应用(这里是 Laravel 项目)进行部署,而且理论上可以启动任意多个处理进程消费消息队列中的任务,所以可以非常方便地通过水平扩展来提高系统并发量,此外,Laravel 还提供了消息队列中间件和频率限制功能,可以对异常流量尖峰进行有效控制,提高消息队列的可用性。
我们可以把数据库优化、缓存(含动态和静态缓存)、消息队列作为 Laravel 应用性能优化的三板斧,合理地组合这套三板斧招式可以有效应对应用性能瓶颈,提升系统吞吐量。

10 Comments
newQuery()这个方法不是静态方法,这是使用会报错。
开始看不懂了
我觉得学院君可以出一个RabbitMQ得入门到实战的教程,RabbitMQ在项目里边用的比较多
都没说清楚是哪个控制器,
php artisan queue:work
Error
Class 'Think\Db' not found 运行 php artisan queue:work 直接报上面的错误,也不知道怎么解决,看得好难受啊
请看 RabbitMQ 入门到放弃
你好 可以公用一个会员吗
处理进程:这一块怎么和你那样在队列处理器窗口看到队列的任务处理记录。是什么命令吗?
我们项目中(lumen)是写了一个异步 Job, 然后通过在 handle()里加 switch case 来实现异步方法的,这样每次想要执行一个异步方法都要加一个,导致这个方法现在很长,有没有好的方法可以直接把方法塞到异步队列里? 虽然可能不是好的实践(但是是很偷懒)
你看看,laravel代码你怎么引用tp的类,晕